- Solutions
- The Company
- About usCartrack offers smart fleet solutions guaranteed to optimise your fleet and workforce, no matter how big or small your business.
- Investor RelationsCartrack has a history of strong cash flow generation and cash conversion, low financial leverage and strong dividends.
- CareersCareers portal. View all the current Cartrack career openings and opportunities available.
- Resources
- Contact Us
- Bahasa
- Login
How to Track Engine Hours and Why They’re Crucial for Your Fleet

---- 2024/03/28 ---
What are engine hours?
Engine hours refer to how long an engine has been running throughout its lifespan or during a specific operation. It is a crucial metric used in various industries relying on machinery and heavy equipment. This metric is important to help you accurately determine your vehicle or equipment usage.
How are engine hours calculated?
Engine hours are calculated based on the number of hours an engine has been running, whether the vehicle is in motion or not. This usage time is typically measured using an engine hour metre. This metre connects to the engine’s ignition system and begins counting hours as soon as the driver turns on the engine.
However, it is important to know that when it comes to engine hours, an hour doesn’t necessarily equate to 60 minutes. An engine hour is determined by a count of the engine crankshaft rotations, which is known as tach time. This means that depending on the engine’s RPM (revolutions per minute), one engine hour can last longer or shorter than a clock hour.
Let’s look at how total engine hours are calculated with an hour metre:
1. Record the starting reading:
Record the hour metre reading at the beginning of your vehicle’s most recent operating period. For example, if the starting reading is 3,421 hours, this is the number used as the initial number of engine hours at the start of the monitoring period.
2. Record the ending reading:
Record the hour metre reading at the end of your vehicle’s operating period. For example, if the reading at the end of your trip is 3,524 hours, this is the number used as the final number of engine hours at the end of the monitoring period.
3. Calculate engine hours for the last drive:
Use the data recorded from the start and end readings to calculate the total engine hours for that specific trip or period. With the above examples, the calculation would be 3,524 hours - 3,421 hours = 103 hours for that specific period.
Are engine hours similar or related to idle hours?
Both engine and idle hours can seem a bit similar, and while these two metrics are very important for understanding a vehicle’s usage, they do have key differences.
Engine hours are used to indicate how long a vehicle’s engine has been running, and whether the vehicle itself is moving or not. This means that engine hours are a measure of the overall running time of the engine, while idle hours only account for the number of hours a vehicle’s engine has been running while the vehicle itself is not moving.
It’s important to note that depending on how drivers operate, along with road conditions, a vehicle’s idle hours will typically be higher than its engine hours.

Why is measuring engine hours so important?
Monitoring engine hours isn’t just another admin task to add to your fleet management list of responsibilities. These measurements play a significant role in the following:
- Maintenance planning:
Vehicles with higher engine usage hours are more prone to unexpected failures due to reduced efficiency. This makes measuring engine hours crucial for vehicle maintenance planning as it provides valuable insights into the actual usage and condition of the engine. Unlike traditional time-based maintenance schedules, which may not account for varying stress levels on the engine, tracking engine hours allows for a more accurate assessment of vehicle wear and tear. By measuring engine hours, you can be more proactive in planning vehicle maintenance, which extends your vehicle's lifespan. This impacts the next benefit of measuring engine hours; cost savings.
- Cost savings:
Vehicle maintenance is a huge fleet expense, so when vehicle maintenance is prioritised, costly breakdowns are prevented and unplanned downtime is eliminated. This means that fleet vehicles can function at their optimum level for longer periods, directly translating to cost savings. Along with this, monitoring engine hours helps in assessing fuel consumption patterns. The more an engine is used, the more fuel it consumes, which leads to lower fuel efficiency. Fuel has been determined to be a fleet's largest expense, accounting for about 60% of a fleet's total operating budget, so they must be able to quickly identify the source of any fuel wastage which in this case, would be an over-utilised engine. By helping fleets not spend too much money on fuel, monitoring engine hours plays a major role in cost savings, leading to improved efficiency and profitability in operations.
- Optimising vehicle usage:
Measuring engine hours gives you accurate insights into how long your vehicle was used. This helps determine which of your vehicles are being used more than others. The over-utilisation of fleet vehicles can lead to accelerated wear and tear, which decreases efficiency, safety and reliability. This means you run the risk of missing customer appointments, making late deliveries, and experiencing unplanned vehicle downtime. By keeping track of which vehicles are being used the most, fleet managers can optimise vehicle dispatching, ensuring that none of their vehicles are at risk of over-utilisation.
- Making informed fleet upgrade decisions:
When you keep an eye on how your engine is being used, you no longer have to play the guessing game when it comes to vehicle upgrades. Engine hour monitoring helps you know exactly when your vehicles need to be upgraded as opposed to just undergoing maintenance. By knowing a vehicle’s exact engine hours, fleet managers can have a better grasp of its actual condition, making spotting potential issues easier. This helps you make quicker data-driven decisions about replacing an ageing fleet vehicle, which leads to an improvement in safety, reliability, and profitability.
- Providing accurate engine logs:
Engine logs are important for measuring engine hours because they provide an accurate record of the engine’s operating time. Inaccurate engine logs can lead to incorrect maintenance schedules, which leads to incorrect maintenance schedules. This can result in increased maintenance costs and reduced vehicle lifespan. For example, if a vehicle’s engine hours are not accurately recorded, the vehicle may not undergo maintenance at the right time, leading to increased wear and tear, and unexpected breakdowns. By keeping accurate engine logs, fleet managers can provide accurate records of fleet vehicle use, which is important for warranty claims and resale value.
- Resale value:
Keeping track of engine hours can help improve fleet resale value by indicating the actual condition of a vehicle and its wear and tear. By tracking engine hours, fleet managers can set up preventative maintenance, optimise vehicle dispatching, and track idling time, which all play a crucial role in maintaining the vehicle’s condition. This means that when it's time to sell a fleet's vehicle, fleet managers do not need to underprice them as they are still running at their optimum level.
Four different types of engine hour metres
There isn’t one single way to calculate engine hours. Here are four of the most common engine hour metres used for this:
- GPS Management:
GPS management can be used as a type of engine hour metre by integrating GPS tracking systems with the vehicle’s engine to provide precise engine hour information and location data. This integration gives fleet managers access to the automated tracking of run time and operating modes, providing an accurate measurement of vehicle usage.
- Hour metre:
The hour metre displays the number of hours the engine has been operating and needs you to record the hours both before and at the end of your trip, as this data is essential to calculating your engine hours.
- Electronic logging devices:
Electronic logging devices, also known as ELDs, are primarily used to record a driver’s hours of service and duty status. These can also be used to record a vehicle’s engine hours, along with its movements.
- Odometers:
As the least common method due to their inaccuracy, odometers are used to measure the distance a vehicle has travelled, only providing a rough estimate of engine use to determine the equivalent distance that the vehicle covered.
What affects engine hours?
There’s a range of factors that can have an impact on your vehicle’s engine hours. These include:
- Engine usage:
The more an engine is used, the more engine hours it accumulates. It is important to remember that both driving and idling times can generate RPMs, which contribute towards engine run time. The higher the number of a vehicle's revs per minute and engine hours, the more wear and tear it may experience.
- Cargo load:
The weight of the cargo being carried can affect how an engine works. The weight of the cargo inside a vehicle affects how hard an engine works, how fast the crankshaft is rotating, and how quickly engine hours can accumulate. Heavier loads require more power from the engine, which contributes to an increase in engine hours. On top of this, fuel efficiency is affected, which can also impact engine hours.
- Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspections are one of the best ways to keep engines running at their optimum levels and keep RPMs and engine hours aligned. Not taking your vehicles for maintenance at a predetermined time can lead to increased wear and tear, which contributes to.
- Engine age:
Like anything else, engines begin to wear out and become less efficient over time. As engines age, they need to work harder to perform the same task, leading to an increase in engine hours. These older engines are also more prone to breakdowns, leading to more frequent maintenance.
- Environment:
Extreme temperatures, dust, and other factors can affect how hard an engine works and how quickly it accumulates hours. For example, engines may accumulate more engine hours in extreme, dusty areas due to the increased workload required to operate in these conditions.
- Vehicle type:
It is important to note that the type of vehicle being used can have a significant impact on the lifespan of its engine. For example, a heavy-duty truck engine may not last as long as smaller cars due to the increased stress and workload they experience.
How long should an engine typically last?
The average lifespan of a vehicle's engine has increased in recent years due to improved technology, improved designs, and enhanced maintenance practices. However, the following insights provide an overview of the typical longevity of vehicle engines:
In the past, the average lifespan of a car’s engine was around eight years or about 241,401 km. However, with advancements in maintenance standards, the average lifespan increased to around 10 years or 321,868 km. On average, a well-maintained petrol-powered truck engine can last about 10-15 years, travelling between 321,868.8 km and 482,803.2 km.
Things to take into consideration with engine hours
When you’re trying to calculate your vehicle’s engine hours, it is important to take the following two factors into consideration:
- Mileage:
Engine hours and mileage are interconnected, and each of these metrics provides valuable insights into a vehicle’s wear and tear, maintenance needs, and overall efficiency. Vehicle mileage refers to the distance a vehicle has travelled and is typically measured in kilometres. By giving us insight into how the vehicle was used in terms of distance, mileage measurements are crucial for assessing vehicle efficiency, which helps fleet managers prioritise maintenance and achieve cost savings.
- Idling time:
Considering idling time when looking at engine hours is important for several reasons. Firstly, idling consumes fuel without contributing to mileage, leading to an increase in fuel costs. Secondly, excessive idling can contribute to increased engine wear and maintenance costs. Engines accumulate hours and wear during idling, which can lead to more frequent maintenance and repairs.
All of this can sound like a lot of work to do, but it doesn’t have to be. The solution to obtaining accurate engine hour recordings for your fleet is a fleet management system.
What is a fleet management system?
Fleet management is a general term for all the tasks that are crucial to the seamless running of a fleet. These activities include keeping vehicles well maintained, keeping an eye on drivers and vehicles at all times, and keeping track of fleet costs. This can sound like a lot of admin, but that’s where a fleet management system comes in. This system is designed to streamline all these processes, making managing a fleet as simple as tapping your laptop keypad.
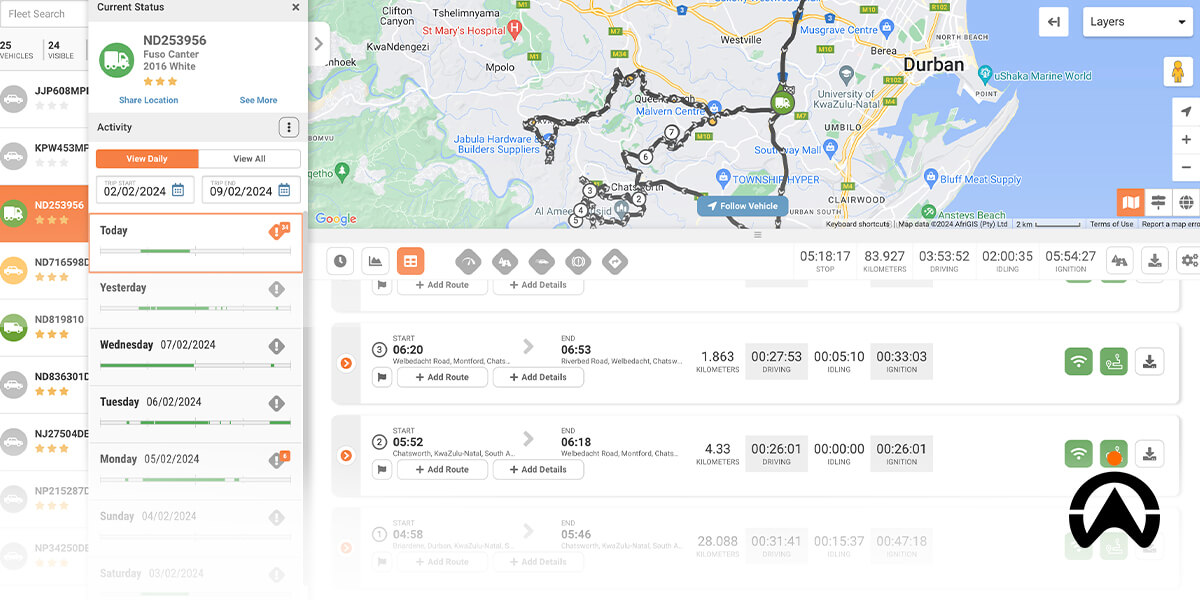
Benefits of a fleet management system
A few of the benefits of a fleet management system include:
- Extending vehicle health: Vehicle health is important for fleet success and longevity, whether you have 1 or 100 vehicles. A fleet management system helps you keep an eye on all your vehicle’s health, helping you spot when they need to undergo maintenance before unplanned breakdowns occur.
- Reduced operational costs: By providing real-time data and analytics, a fleet management system enables efficient cost analysis, which enables data-driven decision-making
- Increased profitability: Fleet management systems help ensure that your fleet is running like a well-oiled machine. This directly translates to an improved bottom line.
- Improved service delivery: A fleet management system ensures that your fleet delivers orders and services on time, giving your customers a positive experience that leaves a lasting impact on your business.
- Improved driver safety: A fleet management system allows you to keep an eye on driver behaviour. By alerting you and them of any dangerous or distracted driving, the likelihood of accidents is reduced, and driver behaviour is significantly improved.
- Fuel consumption monitoring: A fleet management system allows you to closely monitor how much fuel your vehicles are consuming, which helps you spot potential fuel theft and fuel wastage in real time.
Gain accurate insight into your fleet’s engine hours with Cartrack’s solutions
Cartrack is an industry leader when it comes to fleet management, and our solutions are the key you need to unlock full insight into engine hours. Equip you and your business with:
- GPS Tracking: Know exactly how your vehicles have been utilised with Cartrack’s GPS tracking. Real-time GPS tracking can help you monitor vehicle usage by providing up-to-the-minute location updates. Our solution provides you with real-time visibility and total control of your fleet, allowing you to know exactly how long your vehicle was used for, and how effectively it was used. Our GPS tracking also provides you with key performance metrics such as kilometres travelled and idle time. By knowing how much time your vehicles spend idling, you can accurately determine engine hours.
- Preventative maintenance: Keep track of your vehicle’s engine hours with Cartrack’s preventative maintenance. Our platform automates maintenance schedules for vehicles by making use of utilisation hours, engine hours, and the time of the last service. Receive real-time alerts of all engine faults, which helps you pre-empt when your vehicle will need servicing. This means you can keep track of engine hours and use these accurate measurements to set up preventative maintenance schedules, helping you prolong your fleet's lifespan and keep it functioning at its optimum.
- Fuel monitoring: Monitor how much fuel your fleet vehicles are consuming with Cartrack’s fuel monitoring software. An overworked engine has been shown to use more fuel. A fuel monitoring system can help you identify any sudden spikes in fuel consumption. The overworking of an engine can have several impacts on fuel efficiency, including increased fuel consumption, decreased mileage, and unnecessary fuel wastage. Our system provides real-time data on fuel consumption, which allows you to closely monitor fuel usage and identify inefficiencies. It also provides contextualised metrics on fuel consumption per kilometre travelled and per job completed, which helps you correct any inefficiencies.
- Driver ID tags: Ensure your drivers are operating as safely as possible with Cartrack’s driver scorecards. Studies have shown that harsh driving behaviour not only wastes fuel but also increases wear and tear on engine components. Some examples of driver behaviours that negatively impact engine usage include harsh acceleration and cornering, sudden braking, speeding and prolonged idling. These behaviours lead to premature strain being placed on your engine, making it wear out sooner than expected. With our driver scorecards, you can determine how safely your drivers drive while they’re behind the wheel. This is done by keeping track of any high-risk behaviours such as excessive idling and speeding, and harsh braking and acceleration.
Knowing exactly how long your engines are operating is crucial to the longevity and success of your entire fleet.
Get the most accurate readings with Cartrack, and unlock a new level of engine visibility.













 Select Countries
Select Countries